Used Car Export Guide (2023) – Kyrgyzstan
(1) Basic situation
The Kyrgyz Republic (shortened as Kyrgyzstan) is located in Central Asia, bordering Kazakhstan to the north and adjacent to China to the east. Its capital is Bishkek, with a land area of approximately 199,900 square kilometers and a population of 7.2 million people. According to data from the National Statistical Committee of Kyrgyzstan, the country’s GDP in 2023 was $13.98 billion, with a year-on-year growth of 6.2%, and the per capita GDP is about $2,000. According to data published by the Chinese Customs, China remains Kyrgyzstan’s largest trading partner. The total trade volume between China and Kyrgyzstan in 2023 reached $19.8 billion, an increase of 27.8% compared to the previous year. Among them, Kyrgyzstan’s exports to China amounted to $831.8 million, an increase of 30% year-on-year, while China’s exports to Kyrgyzstan were $19.72 billion, up 27.2% year-on-year.
In terms of cooperation, in May 2023, the two sides signed a joint declaration to establish a new era of comprehensive strategic partnership, deepening the partnership. On October 25, 2023, the governments of both countries signed a plan for cooperation in adjacent areas, actively promoting cooperation projects in trade and investment, cross-border transportation, port construction, agriculture, energy, and other fields.
Kyrgyzstan’s natural resources mainly include gold, antimony, tungsten, tin, mercury, uranium, and rare metals. Among them, it ranks third in the world in antimony production and first in the CIS, second in tin and mercury production in the CIS, and third in hydropower resources among CIS countries.

(2) Automobile market conditions
Kyrgyzstan is a left-hand drive country with a relatively weak domestic automotive industry, heavily reliant on imports, especially second-hand vehicles, with a high market share of Japanese brands. Since 2022, there has been a significant increase in automobile imports to Kyrgyzstan.
According to reports from the Kyrgyzstan Economist website, from January to October 2023, Kyrgyzstan imported a total of 143,000 passenger cars, with imports totaling approximately $2 billion. China has become its largest supplier of automobiles, exporting 44,720 vehicles with a transaction value of $688 million.
According to statistics from the Chinese Ministry of Commerce, China exported 71,000 used cars to Kyrgyzstan in 2023. Currently, Chinese automobiles imported into Kyrgyzstan are mainly used for re-export to the Russian market, driven by the huge demand in the Russian automotive market. The local demand for imported vehicles in Kyrgyzstan still has untapped potential.
The capital of Kyrgyzstan, Bishkek, has long been rated as one of the most polluted cities in the world. To address this issue, Kyrgyzstan is actively promoting the development of the new energy vehicle industry. On one hand, it encourages consumers to use electric vehicles by offering preferential import rates for electric cars.
On the other hand, it actively encourages Chinese electric vehicle companies to establish manufacturing plants domestically. However, Kyrgyzstan has only about 30 charging stations nationwide, most of which are located in the capital, Bishkek. Additionally, the country faces energy shortages due to insufficient power generation capacity. The lack of charging infrastructure and energy shortages are the main obstacles hindering the development of Kyrgyzstan’s new energy vehicle industry.
(3) Used car import policies and regulation
1. Import policy
Kyrgyzstan only allows the import of left-hand drive vehicles, with imported used cars not exceeding 10 years in age and meeting at least Euro 2 emission standards. Imported vehicles are subject to inspection. Imported vehicles are classified into temporary and permanent imports. Temporary imports, including motorcycles, must be exported at the end of the agreed period. Kyrgyzstan encourages the import of low-age used cars, imposing higher tariffs on used cars older than 7 years.
2. Tax policy
Temporary import vehicles are subject to a 3% value-added tax and a monthly fee of 0.15% of the contract amount.
Permanent import vehicles are subject to customs duties and value-added tax (VAT). The customs duty is determined based on the age and engine displacement of the vehicle, with the duty being inversely related to the age:
- 1. Vehicles aged less than 3 years are classified as new cars. Customs duty ranges from 10% to 15% of the vehicle’s cost price, depending on the engine displacement.
- 2. Vehicles aged 3-7 years incur a customs duty of 20% of the vehicle’s cost price or a duty based on the vehicle’s specific age, ranging from 0.36 to 0.80 euros/ml. The higher duty between the two options is applied as the import duty.
- 3. Vehicles older than 7 years incur a customs duty ranging from 1.4 to 3.2 euros/ml. Kyrgyzstan’s import VAT for used cars is 12% of the vehicle’s customs price.
- 4. Regarding new energy vehicles, the Eurasian Economic Union region maintains a zero tariff policy for the import of pure electric vehicles until 2025. Kyrgyzstan allows tax-free import of 10,000 new energy vehicles annually and offers tariff incentives for hybrid vehicles.
3. Documents required for import
Original ownership and registration certificates
Original invoice
Driver’s license and international insurance certificate
Bill of lading
Copy of passport
Copy of visa
Original bill of lading (OBL) / air waybill (AWB)
Original technical passport with cancellation mark
Letter of employment
Customs commission letter
If you want to import cars from China, you are welcome to contact us.
Guidelines for Exporting Electric Vehicles from China
Chinese cars are becoming more and more popular in the world, and more and more people are engaged in the business of exporting electric vehicles from China. Below are the guidelines for exporting electric vehicles from China.
Industry Information
On March 28th, Xiaomi Group held a launch event for the listing of Xiaomi Automobiles in Beijing. The Xiaomi SU7 was officially unveiled, and it immediately sparked a sales frenzy in the electric vehicle market. Orders surged rapidly in a short period of time, with crowds gathering at delivery sites, creating unprecedented excitement.
In addition to its popularity in the domestic market, videos testing and reviewing the Xiaomi SU7 have been circulating on overseas platforms such as TikTok and YouTube. Especially notable is its appearance on TikTok in Russia, where local dealers promote it to affluent customers, collecting pre-orders from the Russian market.
According to data released by the General Administration of Customs, in 2023, over 5.22 million Chinese cars were sold overseas, surpassing Japan for the first time and making China the world’s largest exporter of automobiles. In the first quarter of this year, Shanghai alone exported 529,000 vehicles, a year-on-year increase of 30.7%.
Chinese export automobile tariff rate

What are the car tariffs?
The car tariff depends on the landed price of the vehicle. Different brands and models have different landed prices, so the amount of the car tariff varies. Currently, the car tariff in China is 25%, which means the tariff amount is 25% of the landed price of the car.
Additionally, CIF is not the base price of the car; it includes the sea freight and insurance costs on top of the original price. For example, if a car has an original price of 100,000 yuan, with sea freight of 20,000 yuan and insurance of 10,000 yuan, then the tariff would be calculated as follows: (100,000 + 20,000 + 10,000) × 0.25 = 32,500 yuan.
How are car tariffs calculated?
Generally, the comprehensive import tariff for automobiles includes the basic tariff (25%), value-added tax (17%), consumption tax (10%-40%), and other taxes, totaling around 120%.
So, in addition to the 25% basic tariff, automobiles are also subject to value-added tax, consumption tax, and other taxes. The value-added tax rate is 17%, while the consumption tax rate ranges from 10% to 40%. The specific rates of other taxes and the ratio of value-added tax depend on the displacement of the vehicle.

Tariffs are a type of national tax levied by customs on goods and items entering or leaving the border. The tariff rate varies depending on the country and includes customs duties, value-added tax rates, and tariff thresholds.
Value-added tax (VAT) is a turnover tax levied on the value added during the circulation of goods (including taxable services). VAT imposed at the import stage is collected by customs, while VAT at other stages is collected by tax authorities.
Tariffs and VAT standards for common trading countries
(1) United States:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 37.5%, with an average rate of 5.63%. The tariff threshold is $800 USD.
(2) Canada:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 35%, with an average rate of 8.56%. The tariff threshold is 20 Canadian dollars.
(3) Australia:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 10%, with an average rate of 4.6%. Value-added tax (VAT) and consumption tax are levied, with a consumption tax rate of 10%. The tariff threshold is 1000 Australian dollars.
(4) United Kingdom:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 17%. Electronic products such as laptops, mobile phones, digital cameras, and gaming consoles are exempt from tariffs. The standard VAT rate in the UK is 20%. VAT = VAT rate × (CIF value + import duty). The tariff threshold is £135.
(5) Japan:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 30%, with an average rate of 4.49%. Consumption tax = standard consumption tax rate of 8% × (CIF value + import duty). Consumption tax is only levied on alcohol, tobacco, and gasoline. The tariff threshold is 10,000 Japanese yen.
(6) Singapore:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 4%, with an average rate of 0%. VAT = VAT rate of 7% × (CIF value + import duty). The tariff threshold is 400 Singapore dollars.
(7) Malaysia:
Under free trade agreements, different countries are subject to different tariff rates, and consumption tax is replaced by sales and service tax. The sales tax rate is 10%, and the service tax rate is 6%. The tariff threshold is 500 Malaysian ringgit.
(8) Thailand:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 80%, with an average rate of 20.93%. Tariffs are exempted for products such as laptops and other electronic products. VAT = standard VAT rate of 7% × (CIF value + applicable tariff). The tariff threshold is 1,500 Thai baht.
(9) New Zealand:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 15%, with an average rate of 5.11%. VAT = standard VAT rate of 15% × (CIF value + applicable tariff + consumption tax). The tariff threshold is 60 New Zealand dollars.
(10) South Korea:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 40%, with an average rate of 4.17%. VAT = standard VAT rate of 10% × (CIF value + import duty + applicable taxes). The tariff threshold is 150,000 South Korean won.
(11) Germany, France, Italy:
Tariff rates generally range from 0% to 17%. Laptops, mobile phones, digital cameras, and gaming consoles are exempt from tariffs. The standard VAT rates in Germany, France, and Italy are 19%, 20%, and 22% respectively. The tariff threshold is 150 euros.
What procedures and precautions are required for exporting electric vehicles?
Notes on exporting electric vehicles by railway:
- All shipped electric vehicles have passed the safety inspection by the national appraisal institution. The vehicles being shipped are new and are either pure electric vehicles or hybrid vehicles.
- Except for the power batteries and storage batteries installed in the vehicles themselves, no spare batteries or other energy batteries are allowed to be carried. It is imperative to ensure that the charging level does not exceed 65% and provide real photos showing the charging level not exceeding 65%, as well as photos of the matching vehicle identification number (VIN).
- Ensure that the total power of the electric vehicles in the container is turned off.
- The goods name on the customs declaration, item list, and waybill must be completely consistent.
- Reinforcement detail photos (including details of the reinforcement of all four wheels).
- Only new cars can be transported, with a mileage not exceeding 100 km. The trade mode can be for used cars.

Seaborne export requires maritime record filing for electric vehicles:
Electric vehicles fall under Class 9 dangerous goods UN3171 in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, as they are vehicles powered by lithium batteries. Therefore, for the export of electric vehicles, maritime filing must be done to declare them as dangerous goods before they can be shipped out normally.
The export of electric vehicles also requires the following documents:
Export License: Exporting electric vehicles requires obtaining an export license. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the provincial-level (including municipalities directly under the central government) commerce authority in your location.
Customs Declaration Procedures: Exporting electric vehicles requires completing customs declaration procedures. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the customs authorities in your location.
The following is a detailed description of the specific procedures for exporting electric vehicles:
Export License:
Exporting electric vehicles requires obtaining an export license. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the provincial-level (including municipalities directly under the central government) commerce authority in your location.
Conditions for Applying for an Export License:
- The enterprise must have independent legal personality and be registered with the Ministry of Commerce.
- The enterprise must meet the operational requirements specified in the “Measures for the Administration of Export of Electric Vehicles.”
- The enterprise must have the operational and management capabilities suitable for exporting electric vehicles.
Documents Required for Export License Application:
- Copy of the enterprise’s business license.
- Identification of the enterprise’s legal representative.
- Proof of the enterprise’s operating premises.
- Qualifications of the enterprise’s personnel.
- Proof of the enterprise’s financial status.
- Trade contract signed between the enterprise and overseas customers.
- Inspection and qualification report for electric vehicles issued by a designated third-party institution.
- Vehicle Registration Certificate for the vehicles intended for export.
Customs Clearance Procedures:
Exporting electric vehicles requires completing customs clearance procedures. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the customs office in your location.
Documents Required for Customs Clearance of Electric Vehicles:
- Export License
- Invoice
- Contract
- Bill of Lading
- Packing List
- Other relevant supporting documents
Import certification requirements for electric vehicles in some countries/regions
US DOT Certification and EPA Certification:
Entering the US market requires compliance with the US Department of Transportation (DOT) safety certification. This certification is not government-led but is self-tested by manufacturers. The DOT oversees certification for certain components such as windshields and tires. The remaining parts are subject to periodic inspections by the DOT, and any falsification is strictly punished. EPA environmental certification is similar to DOT safety certification, where manufacturers self-declare and are inspected by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
EU E-mark Certification:
Exported vehicles to the EU must obtain e-mark certification for market access. This certification is based on EU directives and involves inspections regarding component approvals and vehicle systems under the EEC/EC Directive. After passing inspection, the product can use the e-mark certificate to enter the EU market.
Nigeria SONCAP Certification:
The SONCAP certificate is a mandatory document for products to clear customs in Nigeria. Without it, delays or rejection may occur. All regulated products covered under the SONCAP program, including automotive spare parts, must undergo inspection and comply with Nigerian national standards or recognized standards to obtain a Certificate of Conformity (COC).
Tanzania PVOC Certification:
Tanzania requires all regulated products covered under the Pre-Export Verification of Conformity to Standards (PVOC) program to undergo inspection. Products must comply with Tanzanian national standards or recognized standards to obtain a Certificate of Conformity (COC) for entry into the Tanzanian market.
Saudi Arabia SABER Certification:
SABER certification is part of Saudi Arabia’s product safety program launched in January 2019. It involves an online certification system for conformity assessment of exported products. Automotive components were included in the certification list in November 2019. The SABER certification process is similar to Nigeria’s SONCAP certification, where products must apply for PC certificates initially and SC certificates for each batch upon shipment.
Customs clearance rules in European countries
In today’s globalized era, international trade has become a crucial link connecting the economies of various countries, with customs clearance rules playing a vital role in this process. Europe, as one of the world’s most important trade regions, its trade activities are not only essential for the economic prosperity of Europe itself but also have a profound impact on the global economy.
EU customs clearance rules
The EU’s customs clearance rules include the influence of the Single Market and Customs Union, the EU Customs Union, as well as the main customs clearance documents and procedures.
1. The impact of the Single Market and Customs Union:
The Single Market:
The European Union’s Single Market is a unified economic area that eliminates tariffs and non-tariff barriers among member states. This means that goods, services, capital, and people can move freely within the European Union without the need for cumbersome customs procedures. This integrated market significantly simplifies trade processes, promoting cross-border trade and economic growth.
Customs Union:
The member states of the European Union form a Customs Union, unifying the tariff policies towards third countries. This means that a uniform tariff rate applies to goods imported into the European Union, regardless of which member state of the EU they enter. This integrated tariff policy reduces uncertainty in foreign trade and provides businesses with a larger market and more opportunities.
2. EU Customs Union:
EU Customs Union is an important institution aimed at facilitating trade circulation. It is committed to coordinating and harmonizing customs procedures among member states to ensure the efficiency and consistency of trade circulation across the entire EU. The EU Customs Union strengthens cooperation among member states through information sharing, training, and technical cooperation, enhancing the supervision and enforcement capabilities against customs violations.
3. Main customs clearance documents and procedures:
Single Window:
The EU adopts the Single Window system, simplifying the declaration process for cross-border trade. Companies can submit all necessary documents and information to all relevant departments with a single declaration, reducing redundant work and time costs.
EU Customs Code:
The EU Customs Code specifies the clearance procedures, declaration requirements, customs responsibilities, and other related aspects of import and export goods. It provides a unified legal framework for trade within the EU and with third countries.
Customs Cooperation Working Party:
This is an institution composed of customs officials from EU member states, aimed at coordinating and promoting customs cooperation within the EU and with third countries. The committee is responsible for developing customs clearance policies, resolving trade disputes, and promoting trade security.
German customs clearance rules

1. Overview of German customs system:
Germany’s customs system is managed and enforced by the Generalzolldirektion (General Customs Directorate) of the Federal Customs Administration (Bundeszollverwaltung). This agency is responsible for overseeing Germany’s customs procedures, including the declaration and inspection of goods for import and export, customs duties collection, and customs compliance reviews.
2. Classification and declaration requirements for import and export products:
Product Classification:
Imports and exports in Germany must be classified according to relevant commodity codes. Germany adopts internationally recognized product coding systems, such as the World Customs Organization’s (WCO) International Harmonized System (HS Code), to ensure consistency and standardization.
Declaration Requirements:
German customs requires the declaration of imported and exported goods to facilitate necessary tariff collection, regulation, and security checks. The declaration typically needs to include detailed descriptions of the goods, their value, quantity, country of origin, and other relevant information. This information is submitted through the relevant customs documents or electronic reporting systems.
3. German customs duties and import taxes:
Tariffs:
Germany, as a member of the European Union, participates in the EU’s Customs Union. Therefore, importing goods from other EU member states usually does not require the payment of additional tariffs. For imported goods from non-EU countries, Germany levies the applicable tariff rates according to the EU’s tariff schedule.
Import Taxes:
In addition to tariffs, Germany may also impose import taxes (such as value-added tax) on specific types of imported goods. The tax rate and scope of import taxes depend on the nature and value of the goods, and are levied in accordance with German tax regulations.
French customs clearance rules

In France, customs regulations are managed and enforced by the Directorate General of Customs and Indirect Taxes (Direction générale des douanes et droits indirects, DGDDI).
1. French customs agencies and organizational structure:
French Customs is the main agency in France responsible for supervising imported and exported goods and enforcing customs regulations. This agency has multiple customs branches and offices, responsible for managing customs affairs in various regions. In addition, France has some special customs agencies, such as the Customs Criminal Investigation Department, which are responsible for combating smuggling and other customs violations.
2. France’s import and export processes and procedures:
Declaration and Inspection:
Imports and exports in France require declaration for customs inspection and supervision. The declaration typically needs to include detailed descriptions of the goods, their value, quantity, origin, and other relevant information. This information is submitted through France’s electronic declaration system or relevant customs documents.
Security Inspection and Audit:
French customs may conduct security inspections and audits on imported and exported goods to ensure compliance and safety. This includes physical inspections or document reviews of specific types of goods to ensure they meet regulatory requirements.
Tariffs and Tax Collection:
France levies applicable tariffs and taxes on imported goods in accordance with the EU’s tariff schedule and domestic tax laws. This may include customs duties, value-added tax (VAT), and other specific taxes, which are imposed based on the nature and value of the goods.
3. France’s special tariffs and tax regulations:
Value Added Tax (VAT):
France imposes value added tax on imported goods, with the rate usually based on the classification and value of the goods. VAT is France’s main consumption tax and applies to domestically produced and imported goods.
Excise Duty:
France may impose excise duty on specific types of goods such as tobacco, alcoholic beverages, and gasoline. These taxes are usually aimed at regulating consumption behavior and protecting public health.
Customs clearance rules in the UK (post-Brexit)

1. Establishment of UK Customs and Borders:
With the United Kingdom’s official departure from the European Union in 2020, the UK government established the UK Border Force and HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC) to manage border and customs affairs. The UK Border Force is responsible for border security and immigration control, while HM Revenue & Customs is responsible for customs duty collection, trade compliance, and border checks.
2. The impact of Brexit on customs clearance rules:
Re-establish the border:
After Brexit, the United Kingdom re-established its borders with European Union member states. This means that import and export goods must comply with new customs clearance procedures, including customs declaration, inspection, and clearance.
New trade relations:
The UK and the EU reached a trade and cooperation agreement, establishing a new trade framework. This has led to changes in some trade processes and tariff policies, impacting businesses’ import and export activities.
Technical and personnel training:
To adapt to the new customs regulations, the UK government has intensified training for customs and trade professionals and invested in new customs technology and facilities to enhance the efficiency and security of border management.
Italian customs clearance rules

1. Italian Customs Agencies and Responsibilities:
The customs authority in Italy is the Guardia di Finanza, which is responsible for supervising and executing the customs procedures for imports and exports, including tariff collection, regulatory compliance oversight, and combating smuggling activities.
2. Requirements for import and export procedures:
Imported and exported goods must comply with Italy’s customs requirements, including proper customs declaration, payment of applicable duties and taxes, adherence to regulatory provisions, and, depending on the nature and value of the goods, obtaining specific permits or certificates.
3. Italy’s special trade zones and preferential policies:
Italy has established several special trade zones, such as free trade zones and bonded areas, which provide favorable conditions and incentives for businesses, thereby promoting the development of trade and investment activities. Additionally, the Italian government has implemented various trade promotion policies, such as tariff exemptions and preferential trade conditions, to encourage the growth of import and export businesses.
Spanish customs clearance rules

1. Organizational structure and functions of Spanish Customs:
Customs management in Spain is the responsibility of the Spanish Tax Agency (Agencia Tributaria), with the Customs and Excise Department (Departamento de Aduanas e Impuestos Especiales) being the main institution in charge of customs affairs. Its functions include, but are not limited to:
- ① Managing and executing the customs clearance procedures for import and export goods, including customs declaration, inspection, and clearance.
- ② Levying duties, value-added tax, and other taxes on imported and exported goods.
- ③ Combating smuggling and other customs violations.
- ④ Providing customs advisory and guidance services.
2. Customs clearance procedures and document requirements in Spain:
Import and export goods must comply with Spain’s customs procedures and document requirements. The main procedures include, but are not limited to:
- ① Submitting customs declarations for import and export goods, including detailed descriptions, value, quantity, and other relevant information.
- ② Depending on the nature and value of the goods, specific permits, certificates, or health and quarantine certificates may be required.
- ③ Payment of applicable duties, value-added tax, and other taxes.
3. Spain’s tariff policies and trade agreements:
EU Customs Union:
As a member of the European Union, Spain participates in the EU Customs Union, implementing a unified customs policy along with other member states. This means that there are no tariffs on trade within the European Union, and for imported goods from non-EU countries, the EU’s tariff schedule applies.
Bilateral Trade Agreements:
Spain has signed a series of bilateral trade agreements with other countries and regions to promote trade cooperation and economic exchange. These agreements may include tariff reductions, preferential trading terms, etc., helping to expand trade volume between Spain and its trading partners.
Special Trade Zones and Preferential Policies:
Spain has established several special trade zones (such as Free Trade Zones, Bonded Warehouses, etc.), providing convenient conditions and preferential policies for businesses, promoting the development of trade and investment activities. Additionally, the Spanish government has implemented some trade promotion policies, such as tariff exemptions, preferential trading conditions, etc., to encourage the growth of import and export businesses.
Overview of customs clearance rules in other European countries
1. Belgium:
Customs Organization and Functions:
Customs affairs in Belgium are managed by the Federal Public Service Finance. The Customs and Excise Administration is the primary agency responsible for customs clearance matters.
Customs Procedures and Documentation Requirements:
Import and export goods must comply with Belgium’s customs procedures and documentation requirements, including applicable customs declarations, tax payments, certificates, and licenses.
Tariff Policy and Trade Agreements:
Belgium, as a member of the European Union, participates in the EU’s Customs Union, implementing a unified tariff policy along with other member states. Additionally, Belgium has signed bilateral trade agreements with other countries, fostering trade cooperation with its trading partners.
2. Netherlands
Customs Organization and Functions:
Customs affairs in the Netherlands are managed by the Netherlands Tax and Customs Administration. Its Customs department is responsible for supervising and executing the clearance procedures for import and export goods.
Customs Procedures and Document Requirements:
Customs procedures and document requirements in the Netherlands are similar to those in other EU countries and include applicable customs declarations, tax payments, certificates, permits, etc.
Tariff Policy and Trade Agreements:
The Netherlands, as a member of the European Union, participates in the EU Customs Union. Additionally, the Netherlands has signed a series of bilateral and multilateral trade agreements with other countries, promoting trade between the Netherlands and its trading partners.
3. Sweden
Customs Organization and Functions:
Customs affairs in Sweden are managed by the Swedish Customs (Swedish Customs Administration). The Customs Administration is responsible for overseeing and executing the customs procedures for the import and export of goods, ensuring compliance and security of the goods.
Customs Procedures and Document Requirements:
Import and export goods must comply with Sweden’s customs procedures and document requirements, including the relevant customs declarations, payment of taxes and fees, certificates, and licenses.
Tariff Policy and Trade Agreements:
Sweden, as a member of the European Union, participates in the EU’s Customs Union. Additionally, Sweden has signed a series of bilateral and multilateral trade agreements with other countries, providing market access and facilitating trade for its trading partners.
Our company specializes in exporting cars from China, please contact us if you are interested.
China’s electric car sales are unstoppable
Recently, the China Passenger Car Association released a car market report, revealing the latest developments in the passenger vehicle market from April 7th to 14th. During this period, the performance of the electric car market was particularly remarkable, with both wholesale and retail penetration rates exceeding 50%. This data was also mentioned by BYD Chairman Wang Chuanfu at the China Electric Vehicle Hundred-Person Forum not long ago.

Specific data
According to the report, from April 1st to 14th, the retail sales volume of passenger vehicles in the market was 516,000 units, a decrease of 11% compared to the same period last year, and a slight decline compared to the same period last month. However, the cumulative retail sales volume for this year reached 5.348 million units, an increase of 10% compared to the same period last year. At the same time, the wholesale volume of passenger vehicles from manufacturers nationwide was 534,000 units, an increase of 13% year-on-year, but also a decrease compared to the same period last month.
In the electric car sector, data shows that from April 1st to 14th, the retail sales volume of electric cars reached 260,000 units, a remarkable increase of 32% compared to the same period last year, and also an increase compared to the same period last month. The cumulative retail sales volume for this year in the electric car sector has reached 2.032 million units, showing a staggering 34% year-on-year growth. Additionally, the wholesale volume of electric cars from manufacturers nationwide was 268,000 units, marking a substantial 43% year-on-year increase, and also an increase compared to the same period last month.
What does the data show?
Based on this data, we can see that the importance of electric cars in the market is increasing. During this period, electric cars accounted for approximately 50.39% of retail sales and an astonishing 50.19% of wholesale sales in the passenger vehicle market. The penetration rate of electric cars in the passenger car market is accelerating, and their market share is continuously increasing.
In the future, with the continuous improvement of electric car technology and the enhancement of supporting infrastructure, we have reason to believe that the market share of electric cars will continue to rise, making them a dominant force in the future automotive market. This undoubtedly will bring new opportunities and challenges to the entire automotive industry, and we look forward to further developments in this field.
Why are there so few Chinese cars in the United States?
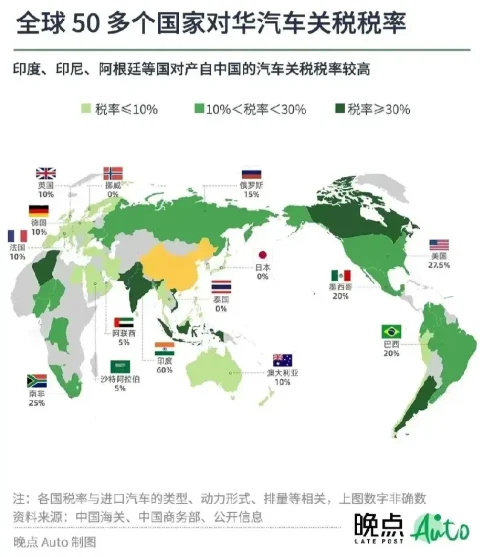
Against the backdrop of globalization, automotive companies have been continuously seeking the best market layout strategies. However, in recent days, several Chinese car manufacturers are considering abandoning the US market and turning to embrace Latin America. Behind this shift lies the imposing tariff barrier of up to 27.5% and the increasingly challenging competitive landscape in the United States.

Faced with this situation, Chinese car companies are seeking new avenues. They have found that while the Latin American market may be relatively small in scale, it holds immense potential and is easier to enter. Therefore, these companies are establishing factories in places like Mexico and Brazil, shifting their focus to this new market full of opportunities.
How are Chinese car companies responding?
Taking BYD as an example, the company is actively preparing to establish a factory in Mexico. According to Zou Zhou, the head of BYD Mexico, overseas production is crucial, and Mexico, as an important market with tremendous potential, is an ideal choice for BYD’s international expansion. It is reported that BYD plans to select a site and begin construction of the factory by the end of the year, with a production capacity of up to 150,000 vehicles per year.
Meanwhile, BYD has also introduced several passenger cars and bus products into the Mexican market, gradually expanding its market share. These products are not only of high quality but also affordably priced, making them popular among local consumers.
In addition to BYD, other Chinese automakers are actively seeking opportunities in the Latin American market. They are establishing research and development centers and production bases in Mexico, Brazil, and other places, strengthening cooperation and communication with local companies to jointly promote the development of the automotive industry.
Have Chinese car companies given up on the U.S. market?
Of course, shifting towards the Latin American market does not mean that Chinese automakers are giving up on their pursuit of the US market. They continue to closely monitor the dynamics of the US market, seeking appropriate timing and methods to enter this market. However, under the current circumstances, the Latin American market undoubtedly represents a more practical and feasible choice.
Facing a 27.5% tariff barrier and intense competition in the US market, several Chinese automakers have chosen to abandon the US market and turn to Latin America. Although this shift may seem somewhat reluctant, it also reflects the flexibility and wisdom of Chinese automakers in responding to changes in the global trade environment.
Is automotive-grade solid-state battery ready to be used soon?
Even novices understand that in the era of new energy vehicles, whoever can solve the three major challenges of battery charging, energy storage, and endurance will become the leader of this era.
Although these three major challenges do not yet have standard answers, the faster the charging, the higher the energy storage, and the more stable the endurance, the higher the competitiveness will be!

Currently, new energy vehicles on the market generally use semi-solid-state batteries, so everyone’s hope is placed on solid-state batteries. Many related enterprises and automakers are also investing in research and development in this area.
What is an all-solid-state battery?
Simply put, all materials that make up the battery are solid-state. In contrast, the structure of current automotive-grade semi-solid-state batteries consists of one electrode side without liquid electrolyte, while the other electrode side contains liquid electrolyte.

In comparison, solid-state batteries offer advantages such as high energy density, strong cycling performance, high tolerance to extreme temperatures, no leakage, and improved safety. The current issues of “rapid degradation in high/low temperatures” and “overstated range” in new energy vehicles stem from the fact that they do not possess the characteristics of solid-state batteries.
Are all-solid-state batteries in mass production?
In fact, solid-state batteries have been applied in multiple fields, but there is currently no mass-produced commercial-grade solid-state battery available.

Although in January this year, ProLogium Technology (China Taiwan) announced the production of the world’s first automotive-grade solid-state battery production line (in Taoyuan, Taiwan), claiming that the new large lithium ceramic battery can be charged to 80% in just 12 minutes, achieving a range of 1000 kilometers and a cycle life of over 1000 times.
However, ProLogium Technology also provided data indicating an annual production capacity of 26,000 units. Currently, this capacity falls far short of meeting the production and sales pace of new energy vehicles.

However, the recently unveiled IM Motors L6 claims to use solid-state batteries, boasting a nearly 900V high-voltage fast charging capability and a range of over 1000 kilometers!
According to the data released by IM Motors L6, the MAX standard version uses lithium iron phosphate batteries (from Contemporary Amperex Technology) and ternary lithium batteries (from CATL), with ranges of 650 kilometers and 780 kilometers, respectively. However, no information regarding solid-state batteries has been provided.
CATL
However, during the performance interpretation meeting of CATL in March this year, Zeng Yuqun stated that, technically, solid-state batteries still face many fundamental scientific issues such as solid-state ion diffusion, and they are far from being commercialized.
We also need to understand that there is an “impossible triangle” in the field of power batteries, which means combining “higher energy density, higher safety, and lower cost” into one battery.
This implies that with the current battery technology, even if mass-produced, high-energy-density, high-safety vehicle-grade solid-state batteries, consumers with ordinary income may not be able to afford them!
This involves research and development investment, material costs, manufacturing costs, and so on. In fact, in the eyes of some industry insiders, rather than focusing on developing vehicle-grade solid-state batteries, it might be more worthwhile to directly leapfrog to hydrogen fuel cells.
According to information released by Sinopec, the company has already reduced the production cost of hydrogen to 1.3 yuan per cubic meter. If they can solve the technical challenges related to transportation, storage, application, and safety on this basis, I believe it would be more worthwhile to vigorously develop hydrogen fuel cells than solid-state batteries. What do you think?
China’s automobile sales in the first quarter of 2024
In the first quarter of 2024, the Chinese automotive industry started steadily, laying a solid foundation for the whole year.

Robust Growth Trend
Specifically, both passenger and commercial vehicle production and sales are showing a robust growth trend. The rapid development trend of electric cars continues, with a stable market share of 30% in China. The country’s overall vehicle exports remain at a high level, continuing to play an active role in driving industry growth. Meanwhile, domestic Chinese brands maintain their growth momentum and retain a higher market share.
Production and Sales Data Overview
According to data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), in March alone, China produced a total of 2.687 million vehicles, an increase of 78.4% compared to the previous month and a 4% increase from the same period last year. In the same month, Chinese automakers sold approximately 2.694 million vehicles, marking a staggering 70.2% year-on-year increase and a 9.9% month-on-month growth. For the first quarter of this year, China’s cumulative vehicle production and sales reached 6.606 million and 6.72 million units, respectively, representing year-on-year growth rates of 6.4% and 10.6%.
Performance of the Electric Vehicle Market
In the past month, Chinese automakers produced and sold 863,000 and 477,000 electric vehicles, respectively, marking year-on-year increases of 28.1% and 35.3%. March saw electric vehicle sales reach 758,000 units, representing a 92.1% month-on-month growth and a 32% year-on-year increase. Concurrently, China exported 124,000 electric vehicles to overseas markets last month, marking year-on-year growth rates of 52% and 59.4%, respectively. For the first three months of 2024, China’s electric vehicle production and sales reached approximately 2.115 million and 2.09 million units, with year-on-year growth rates of 28.2% and 31.8%, respectively. During this period, electric vehicles accounted for 31.1% of the total national automobile sales. In the first quarter of 2024, domestic electric vehicle sales reached 1.783 million units, showing a 33.3% year-on-year increase. Additionally, electric vehicle exports in the first quarter reached 307,000 units, marking a 23.8% year-on-year growth.
China Automobile Export Data
In March 2024, China exported 502,000 vehicles to overseas markets, marking a 33% month-on-month increase and a 37.9% year-on-year increase. Of the vehicles exported last month, approximately 424,000 were passenger cars, showing month-on-month and year-on-year growth rates of 34.6% and 39.3%, respectively. Meanwhile, the export volume of commercial vehicles amounted to 78,000 units, achieving month-on-month and year-on-year growth rates of 24.9% and 31%, respectively. For the first quarter of 2024, China’s cumulative automobile export volume reached 1.324 million units, reflecting a 33.2% year-on-year increase. From the beginning of the year to date, passenger car exports totaled approximately 1.11 million units (up by 34.3% year-on-year), while commercial vehicle exports amounted to approximately 214,000 units (up by 27.5% year-on-year).
Brand Performance
In terms of individual automobile brands, in March 2024, SAIC Group surpassed Chery to claim the title of monthly export champion, with overseas sales reaching 96,000 units, marking a 10.6% year-on-year increase. It is worth noting that SAIC Group’s export volume over the past month accounted for 19.1% of China’s total automobile exports. Additionally, Chinese electric vehicle giant BYD achieved outstanding growth in automobile exports. In March, BYD shipped 39,000 units to foreign markets, representing a remarkable 1.7-fold year-on-year increase.
Why is the share of joint venture cars brands in China declining?
On March 27th, at the 2023 financial report investor conference, Chairman of BYD, Wang Chuanfu, stated, “The accelerated launch of new energy products by Chinese car companies will erode the market share of joint venture brands. Over the next 3-5 years, the market share of joint venture brands will decrease from 40% to 10%, with 30% representing the growth potential for Chinese brands.”

This means that in a few years, the market share of domestic brands will reach 90%, with 9 out of every 10 cars purchased by consumers being domestically produced.
It sounds a bit exaggerated. Could it be that Mr. Wang is just boasting in front of investors?
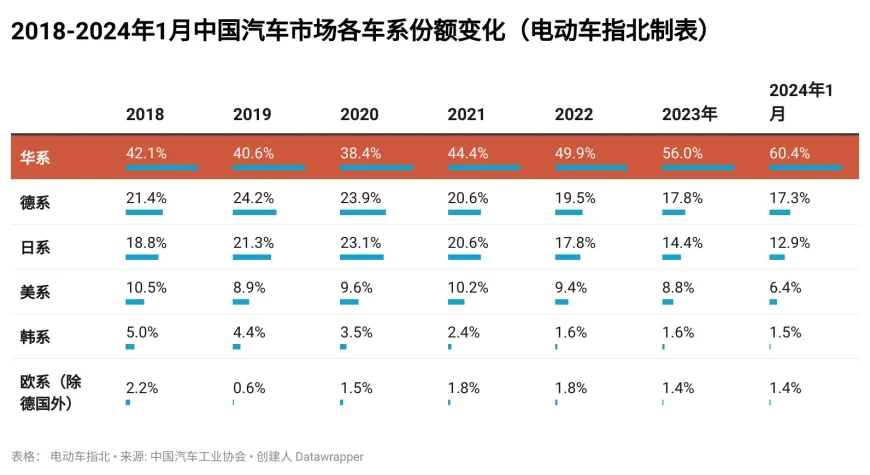
In 3 years, the market share of Chinese brands increased from 38.4% to 60.4%.

The market share of Chinese automotive brands has long struggled around 40%, which has been widely regarded as the “threshold” for Chinese automotive brands. In 2020, it hit a low point for Chinese brands, with a share of only 38.4%. However, it has rapidly increased year by year, reaching 56% in 2023 and even hitting 60.4% in January of this year.
Specifically, from 2020 to January 2024, among joint venture vehicles, the Japanese brands experienced the largest loss in market share, dropping from 23.1% to 12.9%, a decrease of 10.2 percentage points. Following them, German brands also experienced a decline from 23.9% to 17.3%, a decrease of 6.6 percentage points. American and Korean brands also lost 3.2 and 2.0 percentage points, respectively.
The main reason for the rapid loss of market share among joint venture vehicles is their weakness in the electric vehicle sector.
The penetration rate of electric vehicles has reached 45%, and Chinese brands have successfully overtaken the curve.
Based on the number of insurance policies issued, the penetration rate of electric vehicles has consistently exceeded 45% in the past 3 weeks, with the majority being Chinese brands. For example, according to data from the China Passenger Car Association, in February 2024, the penetration rate of electric vehicles among Chinese brands was 55.3%, among luxury cars it was 24%, while among mainstream joint venture brands it was only 4.9%. This means that for every 20 new cars sold by mainstream joint venture brands, 19 are fuel-powered vehicles, and only one is an electric vehicle.
This roughly translates to an inverse relationship between the penetration rate of electric vehicles and that of joint venture cars. For every 1% increase in the penetration rate of electric vehicles, the penetration rate of joint venture cars decreases by nearly 1%. Among them, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Audi’s electric vehicles perform slightly better, but at a considerable cost. For instance, the BMW i3 now starts at just over 210,000 yuan, while the Mercedes-Benz EQE starts at just over 270,000 yuan. These two electric vehicles are both cheaper by around 100,000 yuan compared to their fuel-powered counterparts in the same segment, which can be described as “selling cars at a loss.”
More critically, by 2024, joint venture brands have not produced any competitive electric vehicle products. Currently, joint venture electric vehicles are being labeled as “inferior” products. It can be foreseen that in the coming years, joint venture brands will still rely on fuel-powered vehicles.
The utilization rate of production capacity is collapsing, dealers are withdrawing, and the collapse of joint ventures is accelerating.
Currently, joint venture cars still hold about 40% of the market share, which is actually a very fragile threshold. Once the market share of joint venture cars further decreases, their foundation will be compromised, and the downward trend in the future will only intensify.
There are two key factors contributing to this situation: production capacity utilization and dealerships.
Firstly, the automotive industry heavily relies on economies of scale, as costs are directly linked to production volume. For example, if a factory used to produce 10,000 cars per month, totaling 120,000 cars per year, and suddenly the monthly sales drop to 5,000 cars, the factory’s production capacity would need to decrease to 60,000 cars per year. However, the factory’s annual depreciation expenses and other fixed costs remain constant. Additionally, there would be a reduced need for workers, and the decrease in order quantities could lead to increased prices from suppliers. These factors would significantly increase the cost per vehicle. Therefore, manufacturers often prefer to reduce the retail price of cars to maintain sales volume and utilization of production capacity.

Brutal reality
In the past three years alone, joint venture cars have lost a significant 22 percentage points of market share. Considering China’s annual passenger car volume of about 22 million units, this means that the production capacity of joint venture cars has been forced to decrease by 4.84 million units per year during this period. Many employees at joint venture car factories have reported having “significantly longer holidays” than before. Even Toyota and Honda have started laying off workers. Additionally, Hyundai has sold its factories to companies like NIO, and such occurrences are expected to become more common in the future.
As factory production capacity utilization further declines, the per-vehicle cost for joint venture cars will begin to rise. In the context of a price war, joint venture cars are essentially bleeding on the battlefield, and the outcome is already evident.
However, the bigger crisis for joint venture cars lies in their dealerships.
continued losses
In 2023, joint venture cars were forced to engage in a year-long price war, and many of the costs were borne by the dealerships. For instance, dealerships of Honda reported losing over 10,000 RMB for each Accord sold, even after factoring in rebates, resulting in many of them having to withdraw from the market.
A large number of joint venture car dealerships are facing significant losses, with many owners compelled by their long-term partnerships and the hope of a potential turnaround to say, “We’re willing to stick it out for another year.” However, since 2024, the situation for joint venture cars has not improved but rather worsened. At this point, dealership owners will only accelerate their departure, leading to an increasing rate of closures among joint venture car dealerships.
With dealerships pulling out, joint venture cars undoubtedly become even harder to sell. For many people in smaller towns and areas, the absence of physical stores means they are less likely to consider buying a car, as it creates a lack of trust and security.
Write at the end
Taking a look at China’s neighbors Japan and South Korea, where domestic brands hold a staggering 93% and 83% market share respectively, the decline of joint venture car companies and the rise of domestic brands appear to be a normal commercial phenomenon. In the past, the dominance of joint ventures in the main market was merely a historical accident. What is happening today is simply a correction, with everyone returning to their rightful place.
Therefore, it’s likely that Chairman Wang is not exaggerating this time. The BYD Qin PLUS, priced at 79,800 RMB, has already been accelerating this process. We are all witnesses to history.
How did the Chinese Automotive Industry rise from Zero to Hero?
Not so long ago, the term “Chinese automotive industry” barely registered on the global radar. Fast forward to today, and it’s a completely different story. The rise from zero to hero is a story of strategic maneuvers, cultural transformations, and an unshakable commitment to innovation.
Rewind a few decades, and China’s automotive landscape was quite barren. Cars were a rare luxury that few could afford or think about. However, as if shifting a switch, the country rewrote automotive history, starting with humble beginnings, joint ventures with global huge companies, and a vision that went beyond borders.
The essence of this story is the strategic collaborations made with established automakers from around the world. China absorbed these lessons, combined them with local innovation, and set out on a mission to not only catch up but lead.
Today, Chinese Automotive Technology are not just competing with their competitors but setting benchmarks, especially in the electric and smart vehicles industry.
What is the automotive industry in China?
China is the world’s largest automobile market, both in terms of production and sales. The country’s strong economic growth, rising middle class, and supporting government policies have driven its rise.
While China remains the leader in traditional automotive manufacturing, electric car manufacturers are kicking off in a new era in the industry. China is establishing itself as the focus of EV research and acceptance, thanks to significant investments in EV technology and infrastructure, as well as aggressive government regulations and subsidies.

In 2022, the market share of Chinese cars in the Middle East increased by 80% compared to 2016, with over 350,000 units sold.
In this new era, the Chinese automotive industry has become a hotbed for innovation, especially in the fields of electric vehicles, battery technology, and smart, connected cars. This industry’s shift towards high-tech, environmentally friendly vehicles China became an advocate of global movement towards sustainable transportation.
Chinese automakers are no longer content with dominating the domestic market; they are increasingly looking to expand their footprint on the global stage with Chinese Electric Vehicles (EVs). Brands like Geely, BYD, and Great Wall are becoming household names in various parts of the world. They are also seen as a challenging competitor against established players with their competitive pricing and innovative features.

Who are the key players in China’s EV market, and how are they categorized?
From government backing to Chinese Auto Manufacturers and tech-savvy startups, China’s EV Ecosystem is a bit complex and exciting.
Since the 1990s, the Chinese government has enacted favorable policies to stimulate the expansion of the electric vehicle industry. Under the ambitious “Made in China 2025” vision, initiatives include consumer subsidies, sectoral strategies, and the construction of charging infrastructure, with the goal of EVs accounting for a large share of Smart Cars in China. This push has even resulted in plans to create millions of EV charging stations by 2025, and to create a comprehensive and high-quality charging infrastructure system by 2030.

Who are the key players?
China’s local manufacturers have shown remarkable prowess. They’ve been making strides in areas such as:
- ➔Smart thermal management systems
- ➔Innovative cooling solutions for electric motors
- ➔Integrated onboard chargers and converters
These features are essential for enhancing EV performance and reducing costs. Also, helped in crafting vehicles that not only appeal to the local market but are also competitive globally.
Chinese manufacturers are particularly noted for their focus on customer experience and advanced battery technology, which have been critical in setting them apart from international competitors.
The market itself is vibrant, with battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) taking significant shares.

Leading EV Manufacturers
BYD
BYD has grown from a battery maker to a global EV powerhouse with a diverse variety of EVs. In 2022, BYD outsold Tesla in terms of global sales, a notable milestone. The company’s approach involves a heavy emphasis on vertical integration, including its own batteries and critical components such as insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs). BYD’s success is due to its value-for-money solutions and developing global footprint, with a current focus on markets outside the U.S.
SAIC-GM-Wuling (Joint Venture)
Known for the Hongguang Mini EV, this Joint Ventures in Chinese Automotive industry between SAIC, GM, and Wuling has capitalized on the demand for practical and affordable mini EVs. The Hongguang Mini EV has seen phenomenal sales, becoming the top-selling EV in China in previous years.
Tesla
As the first foreign automaker to fully own an EV factory in China, Tesla enjoys preferential treatment and has become a key player in the Chinese EV market. Focusing on premium EVs, Tesla’s Shanghai Gigafactory contributes significantly to its global production. Despite facing competition from local manufacturers, Tesla continues to expand its presence and capabilities in China.
Nio
This Shanghai-based company specializes in premium smart EVs and is known for its commitment to not engaging in price wars, focusing instead on high-quality, innovative offerings. Nio‘s vehicles are priced in the premium segment and feature advanced autonomous driving capabilities. Despite its premium pricing strategy, Nio has reported significant sales growth and plans to enter the U.S. market by 2025.
Xpeng
With ambitions of expanding its footprint globally, Xpeng has made inroads in Europe starting with Norway. The company aims to deliver half of its vehicles outside China in the future. Known for integrating advanced autonomous driving features and internet technologies, Xpeng’s vehicles are popular among younger consumers.
How is China impacting the global automotive market, especially in Europe?
Over recent years, the market share of BEVs and PHEVs in China has seen substantial growth, indicating a strong and growing consumer acceptance and demand for electric mobility solutions.
China’s EV market is shaped by a mix of:
- ➔Strong government support
- ➔Innovative manufacturing practices
- ➔Growing consumer base
The collaboration of these elements makes the market not only a leader in EV production and adoption but also a fascinating field for future technological advancements and sustainable transport solutions.
What led to the rapid expansion of China’s NEV market in recent years?
The Chinese government has been a significant driver behind the growth of New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) in China, introducing over 600 supportive policies at both the central and local government levels. These policies encompass various aspects, including technological innovation, promotion, application, security, and more.
Initiatives such as:
- ●Offering NEV purchase subsidies
- ●Grants for constructing charging facilities
- ●Facilitating NEV sales in rural areas
The government has also set ambitious targets, like increasing the share of NEVs in total car sales to around 20 percent by 2025, to encourage the adoption of green transportation.

Market Demand and Consumer Acceptance
There’s a growing demand for NEVs among Chinese consumers due to the increasing awareness of energy savings, cost reduction, and pollution reduction benefits.
The younger generations, in particular, are more inclined towards NEVs, not just for the subsidies but also for the environmental advantages they offer.
By the end of 2025, China aims to establish a charging system that can support over 20 million vehicles, further solidifying the foundation for NEV adoption.
Chinese NEV brands like BYD have demonstrated resilience in supply chain management and innovation, contributing to the sector’s growth. Moreover, these brands are increasingly looking to expand their presence globally, with China’s NEV exports showing strong performance, particularly in European markets.
These factors have combined to catapult China EV Market Trends into a period of rapid growth, establishing the country as a leader in the global shift toward greener transportation.
What are the export transportation methods for electric cars?
The export transportation of cars mainly includes the following methods: Ro-Ro transportation, car container transportation, and frame-based transportation.
1. RoRo ship transportation
What is a RoRo ship?
The concept of roll-on/roll-off (Ro-Ro) ships originated from military tanks or vehicle landing crafts. The world’s first Ro-Ro ship was the “Ideal X,” built in the United States in 1958.
Ro-Ro ships, also known as “roll-on, roll-off” ships, or “drive-on, drive-off” ships, are vessels designed for the direct loading and unloading of cargo, such as container trailers or wheeled pallets, using tractor units. Cargo is not lifted vertically onto or off the cargo hold from the deck but is driven on or off the vessel via ramps at the bow, stern, or sides of the ship, and connected to the shore using ramps or gangways. This method utilizes trailers or forklifts to transport containers or goods, along with their wheeled chassis, between the vessel and the shore. For vehicles with their own power, drivers can directly drive on and off the vessel.

Ro-Ro ship structure
Roll-on/roll-off (Ro-Ro) ships typically have multiple decks for cargo placement, with the upper deck featuring a flat surface. Ramps or elevating platforms connect the various decks, allowing vehicles to pass between them. Superstructures are usually arranged at the bow or stern to facilitate cargo stowage. The engine room is located at the stern, with funnels positioned on both sides. The entrances and exits of Ro-Ro ships are usually located at the stern, equipped with articulated ramps to connect with the shore, facilitating the loading and unloading of rolling cargo.

Advantages of RoRo ships
Roll-on/roll-off (Ro-Ro) ships offer several advantages in international automotive transportation, including fast loading and unloading speeds, no need for additional port handling equipment, high transportation quality, visible delivery conditions, convenient supervision and inspection, and minimal cargo damage. As a result, Ro-Ro ships are widely used in international automotive transportation and are currently the most mainstream and conventional method of shipping vehicles by sea.
Situation in China
The advantages of Ro-Ro shipping are evident, but the Chinese automotive industry currently faces a significant shortage of transport capacity in the short term. According to the latest analysis by Clarkson Research, there are only 39 dedicated car carriers (Ro-Ro ships used for automotive exports) in China, with a total of 115,000 car spaces, accounting for 2.8% of global capacity.
The mismatch between maritime shipping capacity and export capacity has led to a significant increase in transportation costs for Chinese automotive exports. Clarkson Research’s latest data shows that from August 2020 to the end of November 2023, the charter rates for a 6,500 standard car capacity car carrier (one-year term) surged from $10,000 per day to $115,000 per day, an increase of over 10 times.
On one hand, the rapid growth in automobile exports has led to soaring Ro-Ro freight rates, while on the other hand, China lacks influence in Ro-Ro shipping. In response to this situation, various Chinese enterprises are entering the Ro-Ro shipping market through methods such as ordering, purchasing, and leasing. In the layout of Ro-Ro shipping enterprises, there are logistics companies as well as the presence of automobile manufacturers.

China’s demand for ro-ro ships
Ro-Ro transportation not only requires transportation carriers but also relies on the support of Ro-Ro terminals. According to incomplete statistics, there are approximately 40 coastal ports in China involved in automobile maritime trade, with ports such as Shanghai Port, Guangzhou Port, Tianjin Port, Yantai Port, Lianyungang Port, and Dalian Port being the main ones. The current overall capacity generally meets the demand, but there are structural problems in the layout of terminals, particularly in the Yangtze River Delta region, where the resource capacity of Ro-Ro terminals is relatively insufficient.
In 2022, exports from automobile companies such as SAIC, Chery, Tesla, and Geely in the Yangtze River Delta region accounted for 58.5% of the total exports in China, while those from companies like Changan and Dongfeng in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River accounted for 14.8%. There is a strong demand for automobile maritime transportation in this region, but the configuration of Ro-Ro terminals is relatively inadequate.
China’s specialized automobile Ro-Ro terminals are in a golden period of development. However, with the slowing economic growth, major automobile terminals will face fierce competition. They need to gradually expand their service scope based on different location advantages and development conditions, gradually extending from passenger cars to engineering machinery, specialized vehicles, and other areas, forming differentiated development approaches and patterns.
2. Car container transportation
Automobile container transportation for exports can be carried out via both sea and railway transportation. Sea container transportation has the advantages of large capacity, multiple routes, and low prices, and China has relatively sufficient capacity in this regard. Railway transportation mainly relies on the China-Europe Railway Express.
Automobile containers can be loaded using standard 20-foot containers.

In general, consignors may choose to load new energy vehicles in 40-foot containers, and there are three common loading schemes:
(1) Two cars in one container:
Two new energy vehicles are loaded side by side in the container, secured to the container using chocks (such as triangular wedges) and straps.

(2) Three cars in one container:
A transport rack is placed inside the container, securely fixed to the container. One car is diagonally loaded onto the transport rack, another car is loaded flat underneath the rack, and a third car is loaded flat near the container door. The vehicles on the rack are secured to the rack using straps, while the flat-loaded vehicles are secured to the container using chocks and straps.

(3) Four cars in one container:
Two transport racks are placed inside the container and securely fixed to the container. Two cars are diagonally loaded onto each transport rack, while two cars are loaded flat underneath the racks. The vehicles on the racks are secured to the racks using straps, while the flat-loaded vehicles are secured to the container using chocks and straps.

The loading methods for three cars in one container and four cars in one container require the use of transport racks to support and secure the vehicles, with two types available: internal-mounted and external-mounted.
For internal-mounted transport racks, the racks are first fixed inside the container, and then the vehicles are loaded onto them. On the other hand, external-mounted racks have the vehicles loaded and secured onto the racks outside the container. Afterward, the entire assembly is pushed into the container and secured in place.
Containerized transportation for electric cars presents a significantly different material efficiency compared to roll-on/roll-off transport. Its transportation scheme still requires optimization, as the container volume is fixed, and different fixed brackets are needed for transporting vehicles. There are challenges in terms of high transportation risks, low control over delivery quality, and difficulties in container unpacking operations at destination ports. Additionally, exporting electric cars requires them to be declared as dangerous goods, with inconsistent procedures and processes across different locations. This results in enterprises needing to provide various materials, leading to significant administrative hurdles.
3. Frame-based transportation of cars
Frame-based transportation is an extension of containerized transportation for automobiles. A notable example is the collapsible car-specific frame developed through collaboration between Taicang Port and COSCO Shipping. It fully considers the mainstream dimensions of automobiles and the high-quality requirements of transportation, adopting a length of 48 feet, capable of loading 3 complete vehicles when laid flat.

Distinct features:
- It can be stacked and loaded in the cargo hold of vessels, making it suitable for use on vessels with cargo holds and allowing for full utilization of cargo space. It is compatible with a wide range of vessel types, offering considerable flexibility.
- Even in ports without dedicated car terminals, as long as the port has specialized container handling equipment, vehicle transportation can be completed.
- Similar to specialized car transport vessels, vehicles are stowed in the cargo hold of the vessel, avoiding exposure to the elements and ensuring the quality of cargo transportation.
- Due to its open design and ample space, it prevents contact with the vehicle body, reducing the risk of scratches or damage.
- The frame is pre-designed with securement and strapping points, ensuring high levels of safety.
- Stackable heavy frames help save terminal space.

Summary
There are certain safety risks associated with the maritime transportation of automobiles, especially for electric vehicles (EVs) which are now mainstream. EVs, powered by lithium-ion batteries and containing a significant amount of electrical equipment, pose a considerable fire hazard. In the event of a fire, extinguishing it becomes significantly challenging. Internationally, electric vehicles are generally classified as hazardous goods for maritime shipping declaration. Whether it’s roll-on/roll-off transport, container shipping, or frame-based transport, besides basic cost considerations, strict adherence to safety transport standards is a crucial issue to address.