Chinese cars are becoming more and more popular in the world, and more and more people are engaged in the business of exporting electric vehicles from China. Below are the guidelines for exporting electric vehicles from China.
Industry Information
On March 28th, Xiaomi Group held a launch event for the listing of Xiaomi Automobiles in Beijing. The Xiaomi SU7 was officially unveiled, and it immediately sparked a sales frenzy in the electric vehicle market. Orders surged rapidly in a short period of time, with crowds gathering at delivery sites, creating unprecedented excitement.
In addition to its popularity in the domestic market, videos testing and reviewing the Xiaomi SU7 have been circulating on overseas platforms such as TikTok and YouTube. Especially notable is its appearance on TikTok in Russia, where local dealers promote it to affluent customers, collecting pre-orders from the Russian market.
According to data released by the General Administration of Customs, in 2023, over 5.22 million Chinese cars were sold overseas, surpassing Japan for the first time and making China the world’s largest exporter of automobiles. In the first quarter of this year, Shanghai alone exported 529,000 vehicles, a year-on-year increase of 30.7%.
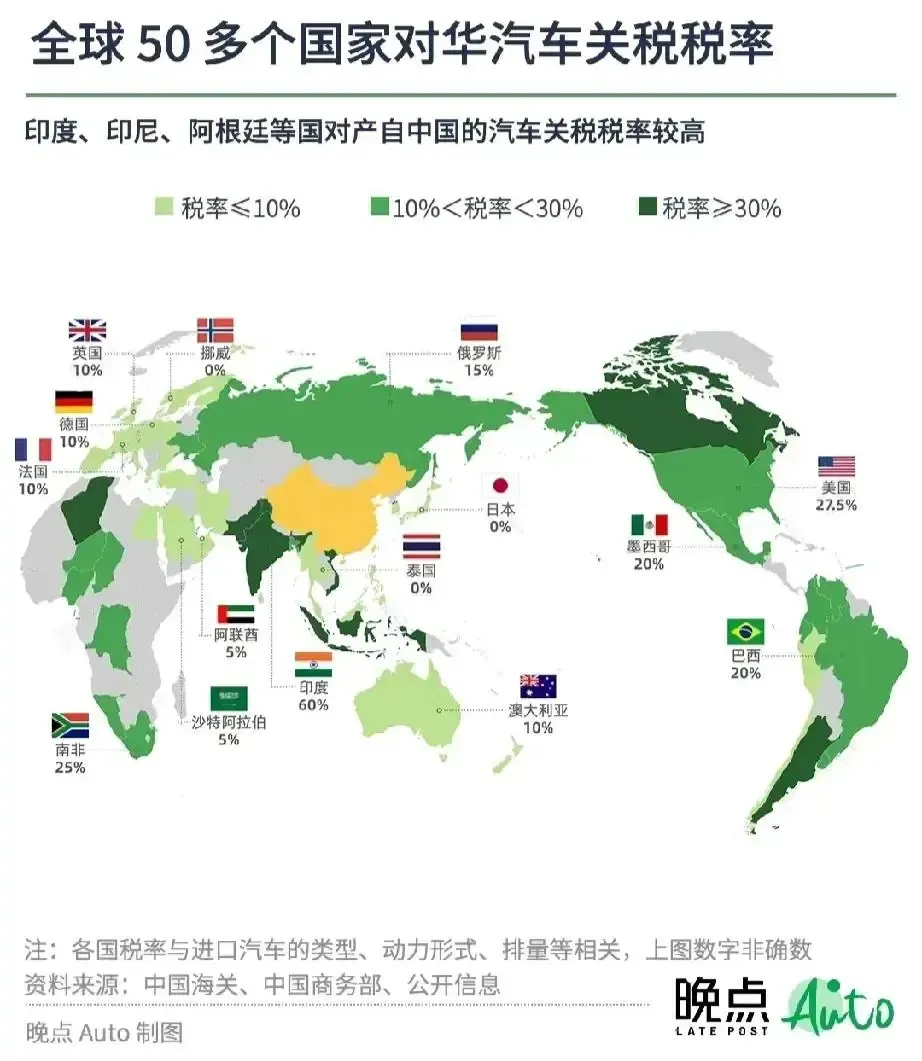
Chinese export automobile tariff rate

What are the car tariffs?
The car tariff depends on the landed price of the vehicle. Different brands and models have different landed prices, so the amount of the car tariff varies. Currently, the car tariff in China is 25%, which means the tariff amount is 25% of the landed price of the car.
Additionally, CIF is not the base price of the car; it includes the sea freight and insurance costs on top of the original price. For example, if a car has an original price of 100,000 yuan, with sea freight of 20,000 yuan and insurance of 10,000 yuan, then the tariff would be calculated as follows: (100,000 + 20,000 + 10,000) × 0.25 = 32,500 yuan.
How are car tariffs calculated?
Generally, the comprehensive import tariff for automobiles includes the basic tariff (25%), value-added tax (17%), consumption tax (10%-40%), and other taxes, totaling around 120%.
So, in addition to the 25% basic tariff, automobiles are also subject to value-added tax, consumption tax, and other taxes. The value-added tax rate is 17%, while the consumption tax rate ranges from 10% to 40%. The specific rates of other taxes and the ratio of value-added tax depend on the displacement of the vehicle.

Tariffs are a type of national tax levied by customs on goods and items entering or leaving the border. The tariff rate varies depending on the country and includes customs duties, value-added tax rates, and tariff thresholds.
Value-added tax (VAT) is a turnover tax levied on the value added during the circulation of goods (including taxable services). VAT imposed at the import stage is collected by customs, while VAT at other stages is collected by tax authorities.
Tariffs and VAT standards for common trading countries
(1) United States:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 37.5%, with an average rate of 5.63%. The tariff threshold is $800 USD.
(2) Canada:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 35%, with an average rate of 8.56%. The tariff threshold is 20 Canadian dollars.
(3) Australia:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 10%, with an average rate of 4.6%. Value-added tax (VAT) and consumption tax are levied, with a consumption tax rate of 10%. The tariff threshold is 1000 Australian dollars.
(4) United Kingdom:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 17%. Electronic products such as laptops, mobile phones, digital cameras, and gaming consoles are exempt from tariffs. The standard VAT rate in the UK is 20%. VAT = VAT rate × (CIF value + import duty). The tariff threshold is £135.
(5) Japan:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 30%, with an average rate of 4.49%. Consumption tax = standard consumption tax rate of 8% × (CIF value + import duty). Consumption tax is only levied on alcohol, tobacco, and gasoline. The tariff threshold is 10,000 Japanese yen.
(6) Singapore:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 4%, with an average rate of 0%. VAT = VAT rate of 7% × (CIF value + import duty). The tariff threshold is 400 Singapore dollars.
(7) Malaysia:
Under free trade agreements, different countries are subject to different tariff rates, and consumption tax is replaced by sales and service tax. The sales tax rate is 10%, and the service tax rate is 6%. The tariff threshold is 500 Malaysian ringgit.
(8) Thailand:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 80%, with an average rate of 20.93%. Tariffs are exempted for products such as laptops and other electronic products. VAT = standard VAT rate of 7% × (CIF value + applicable tariff). The tariff threshold is 1,500 Thai baht.
(9) New Zealand:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 15%, with an average rate of 5.11%. VAT = standard VAT rate of 15% × (CIF value + applicable tariff + consumption tax). The tariff threshold is 60 New Zealand dollars.
(10) South Korea:
Tariff rates range from 0% to 40%, with an average rate of 4.17%. VAT = standard VAT rate of 10% × (CIF value + import duty + applicable taxes). The tariff threshold is 150,000 South Korean won.
(11) Germany, France, Italy:
Tariff rates generally range from 0% to 17%. Laptops, mobile phones, digital cameras, and gaming consoles are exempt from tariffs. The standard VAT rates in Germany, France, and Italy are 19%, 20%, and 22% respectively. The tariff threshold is 150 euros.
What procedures and precautions are required for exporting electric vehicles?
Notes on exporting electric vehicles by railway:
- All shipped electric vehicles have passed the safety inspection by the national appraisal institution. The vehicles being shipped are new and are either pure electric vehicles or hybrid vehicles.
- Except for the power batteries and storage batteries installed in the vehicles themselves, no spare batteries or other energy batteries are allowed to be carried. It is imperative to ensure that the charging level does not exceed 65% and provide real photos showing the charging level not exceeding 65%, as well as photos of the matching vehicle identification number (VIN).
- Ensure that the total power of the electric vehicles in the container is turned off.
- The goods name on the customs declaration, item list, and waybill must be completely consistent.
- Reinforcement detail photos (including details of the reinforcement of all four wheels).
- Only new cars can be transported, with a mileage not exceeding 100 km. The trade mode can be for used cars.

Seaborne export requires maritime record filing for electric vehicles:
Electric vehicles fall under Class 9 dangerous goods UN3171 in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, as they are vehicles powered by lithium batteries. Therefore, for the export of electric vehicles, maritime filing must be done to declare them as dangerous goods before they can be shipped out normally.
The export of electric vehicles also requires the following documents:
Export License: Exporting electric vehicles requires obtaining an export license. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the provincial-level (including municipalities directly under the central government) commerce authority in your location.
Customs Declaration Procedures: Exporting electric vehicles requires completing customs declaration procedures. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the customs authorities in your location.
The following is a detailed description of the specific procedures for exporting electric vehicles:
Export License:
Exporting electric vehicles requires obtaining an export license. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the provincial-level (including municipalities directly under the central government) commerce authority in your location.
Conditions for Applying for an Export License:
- The enterprise must have independent legal personality and be registered with the Ministry of Commerce.
- The enterprise must meet the operational requirements specified in the “Measures for the Administration of Export of Electric Vehicles.”
- The enterprise must have the operational and management capabilities suitable for exporting electric vehicles.
Documents Required for Export License Application:
- Copy of the enterprise’s business license.
- Identification of the enterprise’s legal representative.
- Proof of the enterprise’s operating premises.
- Qualifications of the enterprise’s personnel.
- Proof of the enterprise’s financial status.
- Trade contract signed between the enterprise and overseas customers.
- Inspection and qualification report for electric vehicles issued by a designated third-party institution.
- Vehicle Registration Certificate for the vehicles intended for export.
Customs Clearance Procedures:
Exporting electric vehicles requires completing customs clearance procedures. For specific requirements and procedures, please consult the customs office in your location.
Documents Required for Customs Clearance of Electric Vehicles:
- Export License
- Invoice
- Contract
- Bill of Lading
- Packing List
- Other relevant supporting documents
Import certification requirements for electric vehicles in some countries/regions
US DOT Certification and EPA Certification:
Entering the US market requires compliance with the US Department of Transportation (DOT) safety certification. This certification is not government-led but is self-tested by manufacturers. The DOT oversees certification for certain components such as windshields and tires. The remaining parts are subject to periodic inspections by the DOT, and any falsification is strictly punished. EPA environmental certification is similar to DOT safety certification, where manufacturers self-declare and are inspected by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
EU E-mark Certification:
Exported vehicles to the EU must obtain e-mark certification for market access. This certification is based on EU directives and involves inspections regarding component approvals and vehicle systems under the EEC/EC Directive. After passing inspection, the product can use the e-mark certificate to enter the EU market.
Nigeria SONCAP Certification:
The SONCAP certificate is a mandatory document for products to clear customs in Nigeria. Without it, delays or rejection may occur. All regulated products covered under the SONCAP program, including automotive spare parts, must undergo inspection and comply with Nigerian national standards or recognized standards to obtain a Certificate of Conformity (COC).
Tanzania PVOC Certification:
Tanzania requires all regulated products covered under the Pre-Export Verification of Conformity to Standards (PVOC) program to undergo inspection. Products must comply with Tanzanian national standards or recognized standards to obtain a Certificate of Conformity (COC) for entry into the Tanzanian market.
Saudi Arabia SABER Certification:
SABER certification is part of Saudi Arabia’s product safety program launched in January 2019. It involves an online certification system for conformity assessment of exported products. Automotive components were included in the certification list in November 2019. The SABER certification process is similar to Nigeria’s SONCAP certification, where products must apply for PC certificates initially and SC certificates for each batch upon shipment.